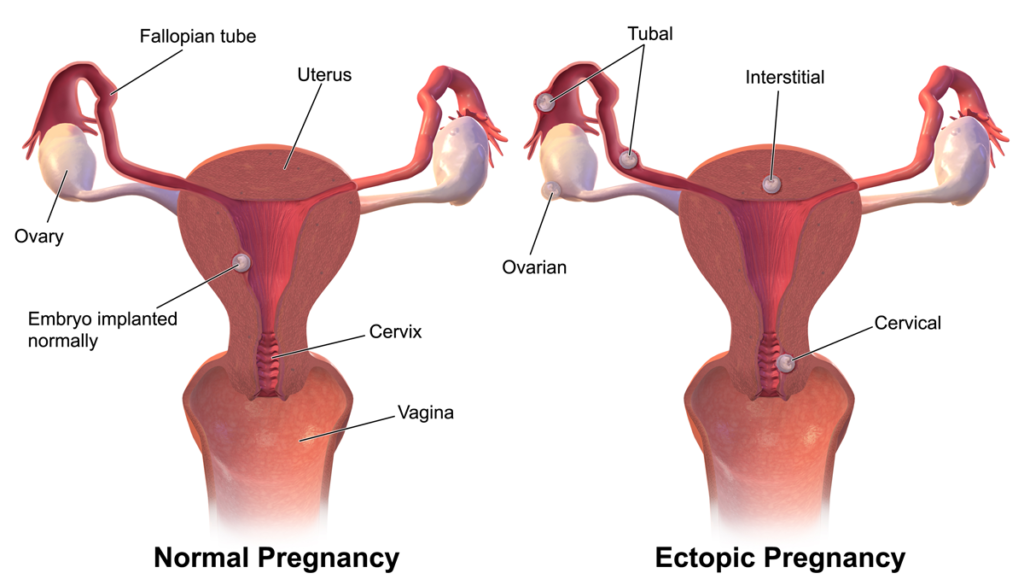
Ectopic pregnancy is an abnormal case of pregnancy in which the fertilized egg does not grow in the uterus’ lining but instead it grows in the fallopian tubes, horns of the uterus, cervix or the ovaries. In order to understand ectopic pregnancy in detail, we need to understand how a normal pregnancy occurs. Normally, the ovaries release eggs into the fallopian tubes; if the egg gets fertilized then it should move into the uterus, where the egg grows for the next 9 months. But this is not the case in an ectopic pregnancy as the fertilized egg remains in the fallopian tubes (tubal pregnancy), horns of the uterus (cornual pregnancy) or the cervix (cervical pregnancy). Tubal pregnancy is the most common ectopic pregnancy.
This type of pregnancy happens in 1 out of every 50 cases. Such pregnancies can’t continue normally and may cause damage to maternal structures. Although, in some cases of tubal pregnancy there are extremely slim chances that the child may survive. Ectopic pregnancies occur in the few weeks of the pregnancy, but doctors usually discover it by the 8th week. However, one can still have a normal and healthy pregnancy in future.
Below are the Ectopic Pregnancy Symptoms, Causes , Treatment, Diagonis and Risk Factors